Efficiency
Enhancement of n-Gaas Characteristics by Combined Heating, Cooling Rate And Metalloporphyrin Modification Techniques
Wed, 2014-07-09 08:58 — Raqi Mohammad Hasan ShubietahDifferent modification techniques, namely, preheating, controlling the cooling rate and modification with tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III) have been used to enhance photoelectrochemical characteristics of n-GaAs electrodes in light-to-electricity conversions. Combination of such three techniques together yielded electrodes with better darkcurrent density vs potential plots and photocurrent density vs potential plots. Higher efficiency and stability were also observed for electrodes modified by such combined techniques.

Enhancement of n-Gaas Characteristics by Combined Heating, Cooling Rate And Metalloporphyrin Modification Techniques
Mon, 2014-03-03 12:07 — Iyad SAADEDDINDifferent modification techniques, namely, preheating, controlling the cooling rate and modification with tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III) have been used to enhance photoelectrochemical characteristics of n-GaAs electrodes in light-to-electricity conversions. Combination of such three techniques together yielded electrodes with better darkcurrent density vs potential plots and photocurrent density vs potential plots. Higher efficiency and stability were also observed for electrodes modified by such combined techniques.

Efficiency of Removal of Cadmium from Aqueous Solutions by Plant Leaves and the Effects of Interaction of Combinations of Leaves on Their Removal Efficiency
Tue, 2014-01-14 10:28 — Mohammed Al-Subu'Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions using 20 species of plant leaves and combinations of these leaves have been studied. Several factors affecting the removal efficiency have been studied. The most efficient types of plant leaves for the removal of cadmium are those of styrax, plum, pomegranate and walnut. The interaction effect of the combined leaf samples on the efficiency of removal of cadmium has been found to be additive in combinations involving styrax plant leaves but seems to be antagonistic in all other combinations. The optimum experimental conditions for removal of cadmium have been found to be at pH 4.1, using high concentrations of naturally dried plant leaves, using ground leaves and to remove cadmium from agitated aqueous solutions. The percentage of metal removed at an initial cadmium concentration of 10 mg/l by the most efficient types of leaves have been found to be 85% for styrax leaves, 85% for plum leaves, 80% for pomegranate leaves, 78% for walnut leaves and 77% for meddler leaves. The presence of foreign ions or complexing agents has been found to reduce the efficiency of removal of cadmium by plant leaves. About 80–85% of the cadmium in charged plant leaves has been released under the influence of changing the pH of the solution, addition of competing ions and the addition of EDTA. The results of removal of cadmium by plant leaves have been found to follow the Freundlich adsorption isotherm, first-order reaction with respect to cadmium and to have intra-pore diffusion as the rate-limiting step.
Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Modified N-Gaas Surfaces: Effect on Photoelectrochemical Efficiency and Surface Stability
Wed, 2013-04-24 11:25 — Samar Al ShakhshirTetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III)sulfate (as an MnIII+MnII ion mixture) was embedded into a polysiloxane polymer matrix and attached to the surfaces of the n-GaAs electrode. The n-GaAs/polymer/MnP system was annealed under nitrogen and used for a photoelectrochemical study in a water/LiClO4/Fe(CN)6 3 −/Fe(CN)6 4− system. The values of short-circuit currents, measured after minutes of illumination, were significantly enhanced by modification. The modified electrode surfaces were more stable to degradation, in the dark and under illumination, than the unmodified ones. Furthermore, the modified electrodes showed higher light-to-electricity conversion efficiency than the unmodified ones. The methodology described here is advantageous in the sense that the semiconductor electrode properties can be enhanced in more than one aspect at the same time.
Multiperturbation Approach to Potential Energy Surfaces for Polyatomic Molecules
Wed, 2013-02-20 09:06 — Mohammed S. Abu-JafarEnhancement of n-Gaas Characteristics by Combined Heating, Cooling Rate And Metalloporphyrin Modification Techniques
Wed, 2011-03-09 09:08 — Hikmat S. Hilal, D.Sc.Different modification techniques, namely, preheating, controlling the cooling rate and modification with tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III) have been used to enhance photoelectrochemical characteristics of n-GaAs electrodes in light-to-electricity conversions. Combination of such three techniques together yielded electrodes with better darkcurrent density vs potential plots and photocurrent density vs potential plots. Higher efficiency and stability were also observed for electrodes modified by such combined techniques.
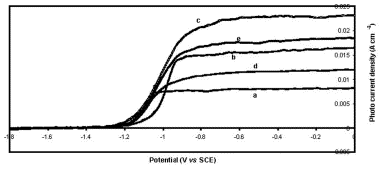
Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Modified N-Gaas Surfaces: Effect on Photoelectrochemical Efficiency and Surface Stability
Wed, 2011-03-09 09:04 — Hikmat S. Hilal, D.Sc.Tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III)sulfate (as an MnIII+MnII ion mixture) was embedded into a polysiloxane polymer matrix and attached to the surfaces of the n-GaAs electrode. The n-GaAs/polymer/MnP system was annealed under nitrogen and used for a photoelectrochemical study in a water/LiClO4/Fe(CN)6 3 −/Fe(CN)6 4− system. The values of short-circuit currents, measured after minutes of illumination, were significantly enhanced by modification. The modified electrode surfaces were more stable to degradation, in the dark and under illumination, than the unmodified ones. Furthermore, the modified electrodes showed higher light-to-electricity conversion efficiency than the unmodified ones. The methodology described here is advantageous in the sense that the semiconductor electrode properties can be enhanced in more than one aspect at the same time.
Effect of Cooling Rate of Pre-Annealed Cds Thin Film Electrodes Prepared by Chemical Bath Deposition: Enhancement of Photoelectrochemical Characteristics
Tue, 2011-03-08 13:20 — Iyad SAADEDDINThin films of CdS, deposited by chemical bath deposition (CBD) onto films of fluorine-doped tin oxide/glass (glass/FTO) substrates were prepared and investigated for photoelectrochemical conversion (PEC) of light into electricity. Knowing the hazardous nature of CdS, the focal theme of this work was to modify the electrodes by simple economic ways to maximize their conversion efficiency and minimize their degradation under PEC conditions. This was to avoid leaching out of hazardous Cd2+ ions. Different parameters have been investigated for this purpose. Multi-deposition preparation, redox couple, and electrode etching affected electrode PEC characteristics. Consistent with earlier literature, annealing the electrode enhanced its conversion efficiency and stability. On the other hand, effect of cooling rate of pre-annealed CdS electrodes, prepared by CBD, on their PEC characteristics has been investigated here for the first time. Controlling the cooling rate was one major factor that affected CdS surface morphology, conversion efficiency and stability under PEC conditions. The major recommendation coming out here is that PEC characteristics of CdS thin film electrodes can be significantly enhanced by pre-annealing the electrode at ∼250 °C followed by its slow cooling.
Effect of cooling rate of pre-annealed CdS thin film electrodes prepared by chemical bath deposition: Enhancement of photoelectrochemical characteristics
Tue, 2011-03-08 13:19 — Amer M EL-HamouzEffect Of Cooling Rate of Pre-Annealed Cds Thin Film Electrodes Prepared by Chemical Bath Deposition: Enhancement of Photoelectrochemical Characteristics
Sat, 2011-02-05 18:08 — Ahed Husni Abdel Razaq ZyoudThin films of CdS, deposited by chemical bath deposition (CBD) onto films of fluorine-doped tin oxide/glass (glass/FTO) substrates were prepared and investigated for photoelectrochemical conversion (PEC) of light into electricity. Knowing the hazardous nature of CdS, the focal theme of this work was to modify the electrodes by simple economic ways to maximize their conversion efficiency and minimize their degradation under PEC conditions. This was to avoid leaching out of hazardous Cd2+ ions. Different parameters have been investigated for this purpose. Multi-deposition preparation, redox couple, and electrode etching affected electrode PEC characteristics. Consistent with earlier literature, annealing the electrode enhanced its conversion efficiency and stability. On the other hand, effect of cooling rate of pre-annealed CdS electrodes, prepared by CBD, on their PEC characteristics has been investigated here for the first time. Controlling the cooling rate was one major factor that affected CdS surface morphology, conversion efficiency and stability under PEC conditions. The major recommendation coming out here is that PEC characteristics of CdS thin film electrodes can be significantly enhanced by pre-annealing the electrode at ∼250 °C followed by its slow cooling.







