Metalloporphyrin
Enhancement of Cdse Film Electrode PEC Characteristics by Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Matrices
Wed, 2014-10-22 12:56 — Dr. Subhi SalehA facile and low-cost strategy to improve stability and conversion efficiency of CdSe film electrodes prepared by chemical bath deposition (CBD) onto FTO/glass substrates, is described. The naked CdSe film electrodes, with band gap value 1.8 eV, photo-corroded under the photoelectrochemical (PEC) working conditions and exhibited no photocurrent. The CdSe film peeled out in short times. Attempts made to enhance stability and efficiency of naked CdSe electrodes, by chemical etching or pre-scratching the FTO surface with fine sand-paper, failed to improve film PEC characteristics. Annealing the glass/FTO/CdSe film also failed to improve its PEC stability or efficiency. When coated with the electro-active species Tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganeseIII/II sulfate embedded inside polysiloxane films (MnPyP/Polysil) the CdSe films did not peel out under the PEC conditions. The coated electrode (glass/FTO/CdSe/MnPyP/Polysil) clearly exhibited photocurrents. Pre-annealing the naked CdSe film at 350 °C, followed by coating with MnPyP/Polysil further enhanced the electrode PEC characteristics. Additional heating of the prepared glass/FTO/CdSe/MnPyP/Polysil electrode at 120 °C also enhanced its PEC characteristics. The mode of action of the MnPyP/Polysil coating has been attributed to its ability to behave as a charge transfer catalyst at the solid/liquid interface. The new technique described here could also be potentially valuable for other types of thin film electrode materials.
Enhancement of Cdse Film Electrode PEC Characteristics by Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Matrices
Wed, 2014-10-22 11:54 — Iyad SAADEDDINA facile and low-cost strategy to improve stability and conversion efficiency of CdSe film electrodes prepared by chemical bath deposition (CBD) onto FTO/glass substrates, is described. The naked CdSe film electrodes, with band gap value 1.8 eV, photo-corroded under the photoelectrochemical (PEC) working conditions and exhibited no photocurrent. The CdSe film peeled out in short times. Attempts made to enhance stability and efficiency of naked CdSe electrodes, by chemical etching or pre-scratching the FTO surface with fine sand-paper, failed to improve film PEC characteristics. Annealing the glass/FTO/CdSe film also failed to improve its PEC stability or efficiency. When coated with the electro-active species Tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganeseIII/II sulfate embedded inside polysiloxane films (MnPyP/Polysil) the CdSe films did not peel out under the PEC conditions. The coated electrode (glass/FTO/CdSe/MnPyP/Polysil) clearly exhibited photocurrents. Pre-annealing the naked CdSe film at 350 °C, followed by coating with MnPyP/Polysil further enhanced the electrode PEC characteristics. Additional heating of the prepared glass/FTO/CdSe/MnPyP/Polysil electrode at 120 °C also enhanced its PEC characteristics. The mode of action of the MnPyP/Polysil coating has been attributed to its ability to behave as a charge transfer catalyst at the solid/liquid interface. The new technique described here could also be potentially valuable for other types of thin film electrode materials.
Enhancement of n-Gaas Characteristics by Combined Heating, Cooling Rate And Metalloporphyrin Modification Techniques
Wed, 2014-07-09 08:58 — Raqi Mohammad Hasan ShubietahDifferent modification techniques, namely, preheating, controlling the cooling rate and modification with tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III) have been used to enhance photoelectrochemical characteristics of n-GaAs electrodes in light-to-electricity conversions. Combination of such three techniques together yielded electrodes with better darkcurrent density vs potential plots and photocurrent density vs potential plots. Higher efficiency and stability were also observed for electrodes modified by such combined techniques.

Enhancement of n-Gaas Characteristics by Combined Heating, Cooling Rate And Metalloporphyrin Modification Techniques
Mon, 2014-03-03 12:07 — Iyad SAADEDDINDifferent modification techniques, namely, preheating, controlling the cooling rate and modification with tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III) have been used to enhance photoelectrochemical characteristics of n-GaAs electrodes in light-to-electricity conversions. Combination of such three techniques together yielded electrodes with better darkcurrent density vs potential plots and photocurrent density vs potential plots. Higher efficiency and stability were also observed for electrodes modified by such combined techniques.

n-GaAs Band-Edge Repositioning by Modification with Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Matrices
Wed, 2013-04-24 12:01 — Samar Al ShakhshirTetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III)sulfate, MnP, (in the forms of MnIII and MnII mixture), was embedded into a polysiloxane polymer matrix and attached to the surfaces of n-GaAs wafers. The n-GaAs=polymer=MnP system was annealed under nitrogen and used for photoelectrochemical study in water=LiClO4=Fe(CN)3 6 = Fe(CN)4 6 system. The results indicated a positive shift in the value of the flat-band potential of the semiconductor due to MnP. This was manifested by shifting the values of the dark-current onset potential and the photo-current open-circuit potential towards more positive values. These findings are potentially valuable in future applications of solar energy in hydrogen and oxygen production from water.
Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Modified N-Gaas Surfaces: Effect on Photoelectrochemical Efficiency and Surface Stability
Wed, 2013-04-24 11:25 — Samar Al ShakhshirTetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III)sulfate (as an MnIII+MnII ion mixture) was embedded into a polysiloxane polymer matrix and attached to the surfaces of the n-GaAs electrode. The n-GaAs/polymer/MnP system was annealed under nitrogen and used for a photoelectrochemical study in a water/LiClO4/Fe(CN)6 3 −/Fe(CN)6 4− system. The values of short-circuit currents, measured after minutes of illumination, were significantly enhanced by modification. The modified electrode surfaces were more stable to degradation, in the dark and under illumination, than the unmodified ones. Furthermore, the modified electrodes showed higher light-to-electricity conversion efficiency than the unmodified ones. The methodology described here is advantageous in the sense that the semiconductor electrode properties can be enhanced in more than one aspect at the same time.
Enhancement of n-Gaas Characteristics by Combined Heating, Cooling Rate And Metalloporphyrin Modification Techniques
Wed, 2011-03-09 09:08 — Hikmat S. Hilal, D.Sc.Different modification techniques, namely, preheating, controlling the cooling rate and modification with tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III) have been used to enhance photoelectrochemical characteristics of n-GaAs electrodes in light-to-electricity conversions. Combination of such three techniques together yielded electrodes with better darkcurrent density vs potential plots and photocurrent density vs potential plots. Higher efficiency and stability were also observed for electrodes modified by such combined techniques.
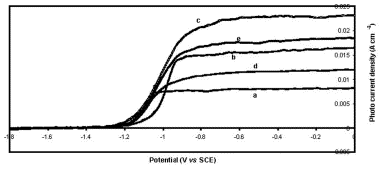
Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Modified N-Gaas Surfaces: Effect on Photoelectrochemical Efficiency and Surface Stability
Wed, 2011-03-09 09:04 — Hikmat S. Hilal, D.Sc.Tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III)sulfate (as an MnIII+MnII ion mixture) was embedded into a polysiloxane polymer matrix and attached to the surfaces of the n-GaAs electrode. The n-GaAs/polymer/MnP system was annealed under nitrogen and used for a photoelectrochemical study in a water/LiClO4/Fe(CN)6 3 −/Fe(CN)6 4− system. The values of short-circuit currents, measured after minutes of illumination, were significantly enhanced by modification. The modified electrode surfaces were more stable to degradation, in the dark and under illumination, than the unmodified ones. Furthermore, the modified electrodes showed higher light-to-electricity conversion efficiency than the unmodified ones. The methodology described here is advantageous in the sense that the semiconductor electrode properties can be enhanced in more than one aspect at the same time.
n-GaAs Band-Edge Repositioning by Modification with Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Matrices
Wed, 2010-04-21 13:32 — Hikmat S. Hilal, D.Sc.Tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III)sulfate, MnP, (in the forms of MnIII and MnII mixture), was embedded into a polysiloxane polymer matrix and attached to the surfaces of n-GaAs wafers. The n-GaAs=polymer=MnP system was annealed under nitrogen and used for photoelectrochemical study in water=LiClO4=Fe(CN)3 6 = Fe(CN)4 6 system. The results indicated a positive shift in the value of the flat-band potential of the semiconductor due to MnP. This was manifested by shifting the values of the dark-current onset potential and the photo-current open-circuit potential towards more positive values. These findings are potentially valuable in future applications of solar energy in hydrogen and oxygen production from water.




