n-GaAs
Enhancement of n-Gaas Characteristics by Combined Heating, Cooling Rate And Metalloporphyrin Modification Techniques
Wed, 2014-07-09 08:58 — Raqi Mohammad Hasan ShubietahDifferent modification techniques, namely, preheating, controlling the cooling rate and modification with tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III) have been used to enhance photoelectrochemical characteristics of n-GaAs electrodes in light-to-electricity conversions. Combination of such three techniques together yielded electrodes with better darkcurrent density vs potential plots and photocurrent density vs potential plots. Higher efficiency and stability were also observed for electrodes modified by such combined techniques.

Enhancement of n-Gaas Characteristics by Combined Heating, Cooling Rate And Metalloporphyrin Modification Techniques
Mon, 2014-03-03 12:07 — Iyad SAADEDDINDifferent modification techniques, namely, preheating, controlling the cooling rate and modification with tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III) have been used to enhance photoelectrochemical characteristics of n-GaAs electrodes in light-to-electricity conversions. Combination of such three techniques together yielded electrodes with better darkcurrent density vs potential plots and photocurrent density vs potential plots. Higher efficiency and stability were also observed for electrodes modified by such combined techniques.

Effect of Annealing And of Cooling Rates on N-Gaas Electrode Photoelectrochemical Characteristics
Mon, 2014-03-03 11:46 — Iyad SAADEDDINThe effect of annealing of the n-GaAs semiconductor on its characteristics in photoelectrochemical (PEC) systems has been investigated. The photocurrent densities vs potential plots were improved by annealing. Cell efficiency and short-circuit current densities were enhanced for the annealed n-GaAs.The effect of the rate of cooling of heated n-GaAs wafers was also investigated. It was found that the slowly cooled electrodes gave better dark current density vs. potential plots, for samples annealed below 600ºC. For samples annealed at higher temperatures, quenching gave better dark-current density vs potential plots. For n-GaAs, slowly cooled electrodes from temperatures below 600ºC showed better photocurrent densityvspotential plots and higher efficiency. n-GaAs samples, quenched from temperatures above 700ºC, showed better photocurrent density vs potential plots and higher efficiency than their slowly cooled counterparts.
Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Modified N-Gaas Surfaces: Effect on Photoelectrochemical Efficiency and Surface Stability
Wed, 2013-04-24 11:25 — Samar Al ShakhshirTetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III)sulfate (as an MnIII+MnII ion mixture) was embedded into a polysiloxane polymer matrix and attached to the surfaces of the n-GaAs electrode. The n-GaAs/polymer/MnP system was annealed under nitrogen and used for a photoelectrochemical study in a water/LiClO4/Fe(CN)6 3 −/Fe(CN)6 4− system. The values of short-circuit currents, measured after minutes of illumination, were significantly enhanced by modification. The modified electrode surfaces were more stable to degradation, in the dark and under illumination, than the unmodified ones. Furthermore, the modified electrodes showed higher light-to-electricity conversion efficiency than the unmodified ones. The methodology described here is advantageous in the sense that the semiconductor electrode properties can be enhanced in more than one aspect at the same time.
Effect of Annealing And of Cooling Rates on N-Gaas Electrode Photoelectrochemical Characteristics
Sun, 2013-03-03 08:44 — Dr. Subhi SalehThe effect of annealing of the n-GaAs semiconductor on its characteristics in photoelectrochemical (PEC) systems has been investigated. The photocurrent densities vs potential plots were improved by annealing. Cell efficiency and short-circuit current densities were enhanced for the annealed n-GaAs.The effect of the rate of cooling of heated n-GaAs wafers was also investigated. It was found that the slowly cooled electrodes gave better dark current density vs. potential plots, for samples annealed below 600ºC. For samples annealed at higher temperatures, quenching gave better dark-current density vs potential plots. For n-GaAs, slowly cooled electrodes from temperatures below 600ºC showed better photocurrent densityvspotential plots and higher efficiency. n-GaAs samples, quenched from temperatures above 700ºC, showed better photocurrent density vs potential plots and higher efficiency than their slowly cooled counterparts.
Enhancement of n-Gaas Characteristics by Combined Heating, Cooling Rate And Metalloporphyrin Modification Techniques
Wed, 2011-03-09 09:08 — Hikmat S. Hilal, D.Sc.Different modification techniques, namely, preheating, controlling the cooling rate and modification with tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III) have been used to enhance photoelectrochemical characteristics of n-GaAs electrodes in light-to-electricity conversions. Combination of such three techniques together yielded electrodes with better darkcurrent density vs potential plots and photocurrent density vs potential plots. Higher efficiency and stability were also observed for electrodes modified by such combined techniques.
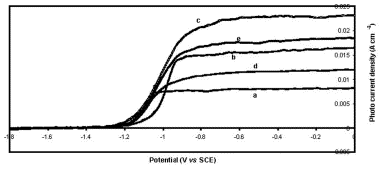
Metalloporphyrin/Polysiloxane Modified N-Gaas Surfaces: Effect on Photoelectrochemical Efficiency and Surface Stability
Wed, 2011-03-09 09:04 — Hikmat S. Hilal, D.Sc.Tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III)sulfate (as an MnIII+MnII ion mixture) was embedded into a polysiloxane polymer matrix and attached to the surfaces of the n-GaAs electrode. The n-GaAs/polymer/MnP system was annealed under nitrogen and used for a photoelectrochemical study in a water/LiClO4/Fe(CN)6 3 −/Fe(CN)6 4− system. The values of short-circuit currents, measured after minutes of illumination, were significantly enhanced by modification. The modified electrode surfaces were more stable to degradation, in the dark and under illumination, than the unmodified ones. Furthermore, the modified electrodes showed higher light-to-electricity conversion efficiency than the unmodified ones. The methodology described here is advantageous in the sense that the semiconductor electrode properties can be enhanced in more than one aspect at the same time.
Effect of Annealing and of Cooling Rates on n-GaAs Electrode Photoelectrochemical Characteristics
Wed, 2010-04-21 13:32 — Hikmat S. Hilal, D.Sc.The effect of annealing of the n-GaAs semiconductor on its characteristics in photoelectrochemical (PEC) systems has been investigated. The photocurrent densities vs. potential plots were improved by annealing. Cell efficiency and short-circuit current densities were enhanced for the annealed n-GaAs. The effect of the rate of cooling of heated n-GaAs wafers was also investigated. It was found that the slowly cooled electrodes gave better dark current density vs. potential plots, for samples annealed below 600 C. For samples annealed at higher temperatures, quenching gave better dark-current density vs. potential plots. For n-GaAs, slowly cooled electrodes from temperatures below 600 C showed better photocurrent density vs. potential plots and higher efficiency. n-GaAs samples, quenched from temperatures above 700 C, showed better photocurrent density vs. potential plots and higher efficiency than their slowly cooled counterparts.




